Semi Infinite Solid
A method that considers space and time.
- Dr. Paul
In contrast to lumped capacitance method which only works on problems that are a function of time, semi-infinite solid method works on problems that are a function of both location and time.
Semi-Infinite Solid is an analysis method that uses a solid that is of infinite size in all but one direction. It is used to analyze temperature of an object over time.
This method yields an analytical solution rather than an approximation, although you are still making an approximation in the fact that infinite solids do not exist. Unlike the lumped capacitance method it can be used where there is a temperature gradient across the solid we are analyzing (the biot number is not very small).
Below are example transient temperature distribution for constant surface temperature (1), constant surface heat flux (2), and surface convection (3).
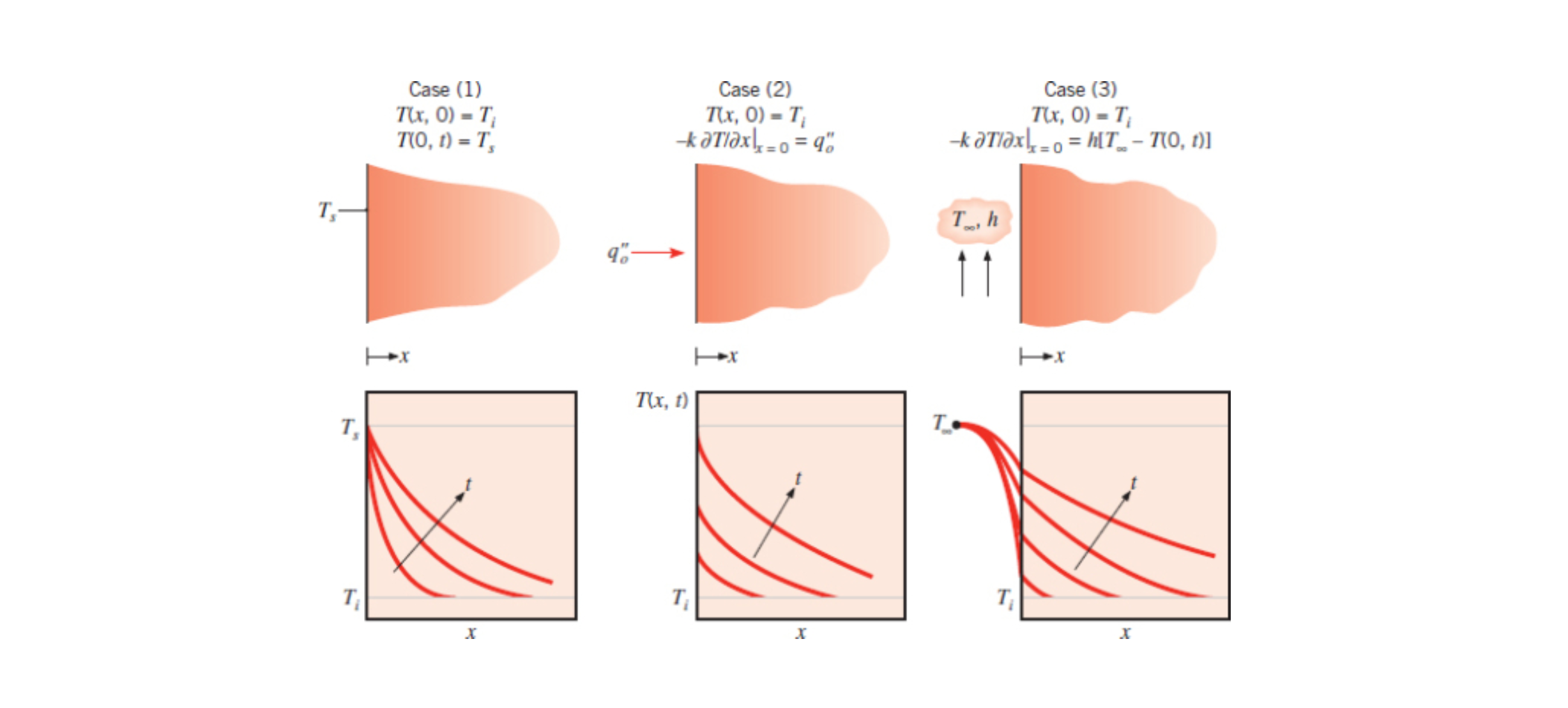
See Section 5.7, 6E - Class 2, 7A - 2nd Class, and 7C - 2nd Class.
Temperature distribution
The derivation for the following equations (and what the error function is and where it came from) can be found in 7A - 2nd Class.
Equation 5.60:
Where
Case 1 Constant Surface Temperature (Eq. 5.61):
Case 2 Constant Surface Heat Flux (Eq. 5.62):
Case 3 Surface Convection (Eq. 5.63):
Where
Python
Equation 5.63 (Case 3 above):
def caseThree(T, Ti, Too, x, alpha, t, h, k):
coeffOne = erfc(x/(2*sqrt(alpha * t)))
coeffTwo = exp(((h*x)/k) + ((h**2 * alpha*t)/k**2))
coeffThr = erfc((x/2*sqrt(alpha*t)) + ((h*sqrt(alpha*t))/k))
coeffFou = (T-Ti)/(Too-Ti)
return coeffOne - coeffTwo * coeffThr - coeffFou